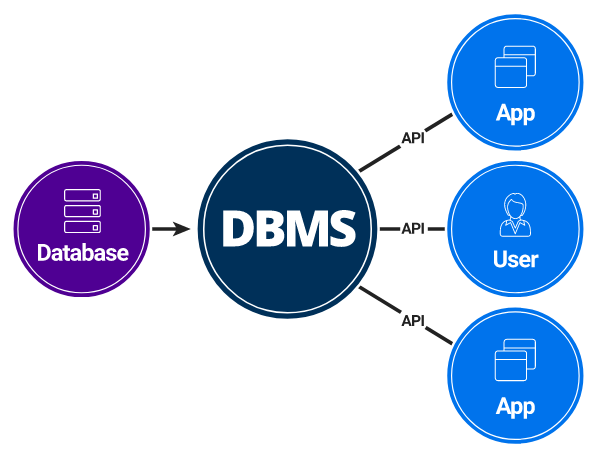
Database Management System (DBMS) is a software for storing and retrieving users' data while considering appropriate security measures. It consists of a group of programs which manipulate the database. The DBMS accepts the request for data from an application and instructs the operating system to provide the specific data. In large systems, a DBMS helps users and other third-party software to store and retrieve data.
DBMS allows users to create their own databases as per their requirement. The term “DBMS” includes the user of the database and other application programs. It provides an interface between the data and the software application.
Database - A database is a collection of related data which represents some aspect of the real world. A database system is designed to be built and populated with data for a certain task.
Characteristics of Database Management System
Provides security and removes redundancy
Self-describing nature of a database system
Insulation between programs and data abstraction
Support of multiple views of the data
Sharing of data and multiuser transaction processing
DBMS allows entities and relations among them to form tables.
It follows the ACID concept ( Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability).
DBMS supports multi-user environment that allows users to access and manipulate data in parallel.
Application of DBMS
Banking - For customer information, account activities, payments, deposits, loans, etc.
Airlines - For reservations and schedule information.
Universities - For student information, course registrations, colleges and grades.
Telecommunication - It helps to keep call records, monthly bills, maintaining balances, etc.
Finance - For storing information about stock, sales, and purchases of financial instruments like stocks and bonds.
Sales - Use for storing customer, product & sales information.
Manufacturing - It is used for the management of supply chain and for tracking production of items. Inventories status in warehouses.
HR Management - For information about employees, salaries, payroll, deduction, generation of paychecks, etc.
Types of DBMS
There are 7 Different types of Database Management System, Which are described below:
Hierarchical Databases
Network Databases
Relational Databases
Object-oriented Databases
Graph Databases
ER model Databases
Document Databases
Hierarchical DBMS
In a Hierarchical database, model data is organized in a tree-like structure. Data is Stored Hierarchically (top down or bottom up) format. Data is represented using a parent-child relationship. In Hierarchical DBMS parent may have many children, but children have only one parent.
Network Model
The network database model allows each child to have multiple parents. It helps you to address the need to model more complex relationships like as the orders/parts many-to-many relationship. In this model, entities are organized in a graph which can be accessed through several paths.
Relational model
Relational DBMS is the most widely used DBMS model because it is one of the easiest. This model is based on normalizing data in the rows and columns of the tables. Relational model stored in fixed structures and manipulated using SQL.
Object-Oriented Model
In Object-oriented Model data stored in the form of objects. The structure which is called classes which display data within it. It defines a database as a collection of objects which stores both data members values and operations.
Graph Databases
Graph databases are NoSQL databases and it uses the graphical structure for semantic queries. Data is stored in the form of nodes, edges, and properties in which node is equivalent to a record, the edge is a link between two nodes and properties are additional information added into the nodes.
ER Model Databases
Entity-Relations Model Database was developed by Peter Chen 1976. Here, the ER model is applied as a database. Each row in the table represents one instance of an object type, and each column in a table represents an attribute type.
Document Databases
Document databases (DBs) are also a NoSQL database. It stores data in the form of documents which are key values. Each document makes the relationship of the data with other data elements and attributes.
It became popular due to its storage of documents and NoSQL properties. The specialty of NoSQL data storage is that it provides a faster mechanism for storing and searching for documents.
Advantages of DBMS
DBMS offers a variety of techniques to store & retrieve data
DBMS serves as an efficient handler to balance the needs of multiple applications using the same data
Uniform administration procedures for data
Application programmers never exposed to details of data representation and storage.
A DBMS uses various powerful functions to store and retrieve data efficiently.
Offers Data Integrity and Security
The DBMS implies integrity constraints to get a high level of protection against prohibited access to data.
A DBMS schedules concurrent access to the data in such a manner that only one user can access the same data at a time
Reduced Application Development Time
Disadvantage of DBMS
DBMS may offer plenty of advantages but, it has certain flaws-
Cost of Hardware and Software of a DBMS is quite high which increases the budget of your organization.
Most database management systems are often complex systems, so the training for users to use the DBMS is required.
In some organizations, all data is integrated into a single database which can be damaged because of electric failure or database is corrupted on the storage media
Use of the same program at a time by many users sometimes lead to the loss of some data.
DBMS can't perform sophisticated calculations
Read more Topics:
DBMS LANGUAGES - https://www.thetechplatform.com/post/dbms-database-languages
DBMS ARCHITECTURE - https://www.thetechplatform.com/post/dbms-architecture
DBMS 3 SCHEMA ARCHITECTURE - https://www.thetechplatform.com/post/three-schema-architecture-of-dbms
DATA MODELING - https://www.thetechplatform.com/post/data-modelling
RELATION DATA MODEL - https://www.thetechplatform.com/post/relation-data-model
NORMALIZATION - https://www.thetechplatform.com/post/normalization
TRANSACTION PROCESSING- https://www.thetechplatform.com/post/transaction-processing
CONCURRENCY CONTROL - https://www.thetechplatform.com/post/concurrency-control
FILE ORGANIZATION - https://www.thetechplatform.com/post/file-organization-in-dbms
THE TECH PLATFORM