What are different types of Loops in Python?
- The Tech Platform

- Oct 14, 2022
- 2 min read
Programming languages provide various control structures that allow for more complicated execution paths. A loop statement allows us to execute a statement or group of statements multiple times. Python provides 3 ways for executing the loops:
For Loop
While Loop
Nested Loop
Types of Loop
Python programming language provides following types of loops to handle looping requirements.
1. For Loop
This is traditionally used when programmers had a piece of code and wanted to repeat that 'n' number of times.
Code:
fruits = ["Apple", "Orange", "Banana"]
print("Example of FOR Loop")
for x in fruits:
print(x)Output:

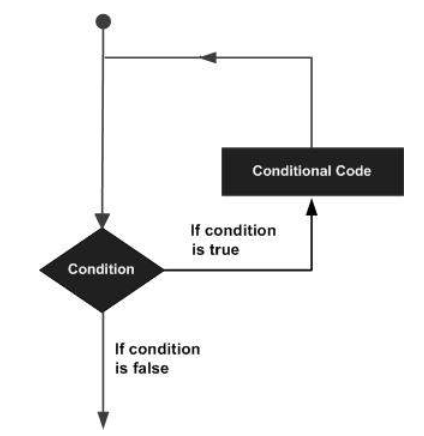
2. While Loop
The loop gets repeated until the specific Boolean condition is met.
Code:
count = 0
while (count < 3):
count = count + 1
print("Banana")Output:

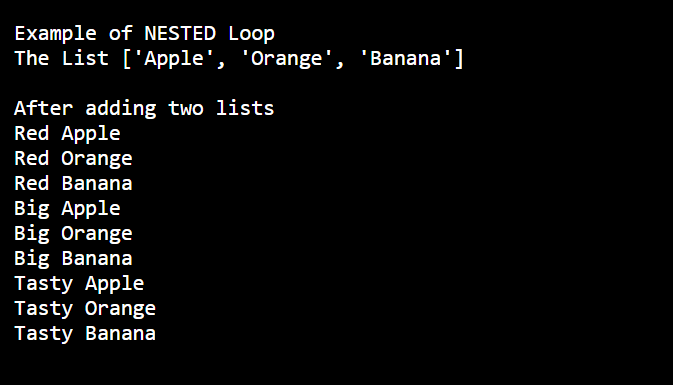
3. Nested Loop
Programmers can use one loop inside another; i.e., they can use for loop inside while or vice - versa or for loop inside for loop or while inside while.
Code:
adj = ["Red", "Big", "Tasty"]
fruits = ["Apple", "Orange", "Banana"]
print("Example of NESTED Loop")
print("The List",fruits, "\n")
print("After adding two lists")
for x in adj:
for y in fruits:
print(x, y)Output:
Loop Control Statement
Loop control statements change execution from its normal sequence. When execution leaves a scope, all automatic objects that were created in that scope are destroyed.
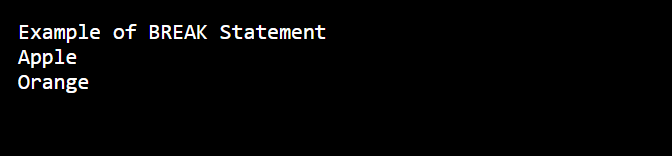
1. Break Statement
It terminates the loop statement and transfers execution to the statement immediately following the loop.
Code:
fruits = ["Apple", "Orange", "Banana"]
print("Example of BREAK Statement")
for x in fruits:
print(x)
if x == "Orange":
breakOutput:
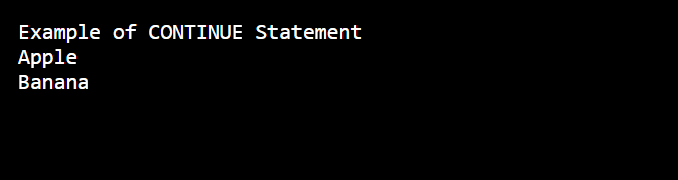
2. Continue Statement
The Continue Statement causes the loop to skip the remainder of its body and immediately retest its condition prior to reiterating.
Code:
fruits = ["Apple", "Orange", "Banana"]
print("Example of CONTINUE Statement")
for x in fruits:
if x == "Orange":
continue
print(x) Output:
3. Pass Statement
The Pass Statement is used when a statement is required syntactically but you do not want any command or code to execute.
Code:
for x in [0, 1, 2]:
passHappy Learning Happy Reading!
The Tech Platform




Comments