Use the Azure Cosmos Emulator for local development and testing
- The Tech Platform

- May 3, 2020
- 13 min read
The Azure Cosmos Emulator provides a local environment that emulates the Azure Cosmos DB service for development purposes. Using the Azure Cosmos Emulator, you can develop and test your application locally, without creating an Azure subscription or incurring any costs. When you're satisfied with how your application is working in the Azure Cosmos Emulator, you can switch to using an Azure Cosmos account in the cloud.
You can develop using Azure Cosmos Emulator with SQL, Cassandra, MongoDB, Gremlin, and Table API accounts. However at this time the Data Explorer view in the emulator fully supports clients for SQL API only.
How the emulator works
The Azure Cosmos Emulator provides a high-fidelity emulation of the Azure Cosmos DB service. It supports identical functionality as Azure Cosmos DB, including support for creating and querying data, provisioning and scaling containers, and executing stored procedures and triggers. You can develop and test applications using the Azure Cosmos Emulator, and deploy them to Azure at global scale by just making a single configuration change to the connection endpoint for Azure Cosmos DB.
While emulation of the Azure Cosmos DB service is faithful, the emulator's implementation is different than the service. For example, the emulator uses standard OS components such as the local file system for persistence, and the HTTPS protocol stack for connectivity. Functionality that relies on Azure infrastructure like global replication, single-digit millisecond latency for reads/writes, and tunable consistency levels are not applicable.
You can migrate data between the Azure Cosmos Emulator and the Azure Cosmos DB service by using the Azure Cosmos DB Data Migration Tool.
You can run Azure Cosmos Emulator on the Windows Docker container, see the Docker Hub for the docker pull command and GitHub for the Dockerfile and more information.
Differences between the emulator and the service
Because the Azure Cosmos Emulator provides an emulated environment running on the local developer workstation, there are some differences in functionality between the emulator and an Azure Cosmos account in the cloud:
Currently Data Explorer in the emulator supports clients for SQL API. The Data Explorer view and operations for Azure Cosmos DB APIs such as MongoDB, Table, Graph, and Cassandra APIs are not fully supported.
The Azure Cosmos Emulator supports only a single fixed account and a well-known master key. Key regeneration is not possible in the Azure Cosmos Emulator, however the default key can be changed using the command-line option.
The Azure Cosmos Emulator is not a scalable service and will not support a large number of containers.
The Azure Cosmos Emulator does not offer different Azure Cosmos DB consistency levels.
The Azure Cosmos Emulator does not offer multi-region replication.
As your copy of the Azure Cosmos Emulator might not always be up-to-date with the most recent changes in the Azure Cosmos DB service, you should refer to the Azure Cosmos DB capacity planner to accurately estimate the production throughput (RUs) needs of your application.
When using the Azure Cosmos Emulator, by default, you can create up to 25 fixed size containers (only supported using Azure Cosmos DB SDKs), or 5 unlimited containers using the Azure Cosmos Emulator. For more information about changing this value, see Setting the PartitionCount value.
System requirements
The Azure Cosmos Emulator has the following hardware and software requirements:
Software requirements
Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2016, or Windows 10
64-bit operating system
Minimum Hardware requirements
2-GB RAM
10-GB available hard disk space
Installation
You can download and install the Azure Cosmos Emulator from the Microsoft Download Center or you can run the emulator on Docker for Windows. For instructions on using the emulator on Docker for Windows, see Running on Docker.
Note To install, configure, and run the Azure Cosmos Emulator, you must have administrative privileges on the computer. The emulator will create/add a certificate and also set the firewall rules in order to run its services; therefore it's necessary for the emulator to be able to execute such operations.
Running on Windows
To start the Azure Cosmos Emulator, select the Start button or press the Windows key. Begin typing Azure Cosmos Emulator, and select the emulator from the list of applications.
When the emulator is running, you'll see an icon in the Windows taskbar notification area.
The Azure Cosmos Emulator by default runs on the local machine ("localhost") listening on port 8081.
The Azure Cosmos Emulator is installed to C:\Program Files\Azure Cosmos DB Emulator by default. You can also start and stop the emulator from the command-line. For more information, see the command-line tool reference.
Start Data Explorer
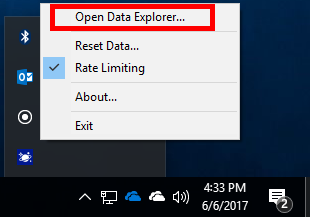
When the Azure Cosmos Emulator launches, it automatically opens the Azure Cosmos Data Explorer in your browser. The address appears as https://localhost:8081/_explorer/index.html. If you close the explorer and would like to reopen it later, you can either open the URL in your browser or launch it from the Azure Cosmos Emulator in the Windows Tray Icon as shown below.
Checking for updates
Data Explorer indicates if there is a new update available for download.
Note Data created in one version of the Azure Cosmos Emulator (see %LOCALAPPDATA%\CosmosDBEmulator or data path optional settings) is not guaranteed to be accessible when using a different version. If you need to persist your data for the long term, it is recommended that you store that data in an Azure Cosmos account, rather than in the Azure Cosmos Emulator.
Authenticating requests
As with Azure Cosmos DB in the cloud, every request that you make against the Azure Cosmos Emulator must be authenticated. The Azure Cosmos Emulator supports a single fixed account and a well-known authentication key for master key authentication. This account and key are the only credentials permitted for use with the Azure Cosmos Emulator. They are:
Account name: localhost:<port>
Account key: C2y6yDjf5/R+ob0N8A7Cgv30VRDJIWEHLM+4QDU5DE2nQ9nDuVTqobD4b8mGGyPMbIZnqyMsEcaGQy67XIw/Jw==
Note The master key supported by the Azure Cosmos Emulator is intended for use only with the emulator. You cannot use your production Azure Cosmos DB account and key with the Azure Cosmos Emulator.
Note If you have started the emulator with the /Key option, then use the generated key instead of C2y6yDjf5/R+ob0N8A7Cgv30VRDJIWEHLM+4QDU5DE2nQ9nDuVTqobD4b8mGGyPMbIZnqyMsEcaGQy67XIw/Jw==. For more information about /Key option, see Command-line tool reference.
As with the Azure Cosmos DB, the Azure Cosmos Emulator supports only secure communication via TLS.
Running on a local network
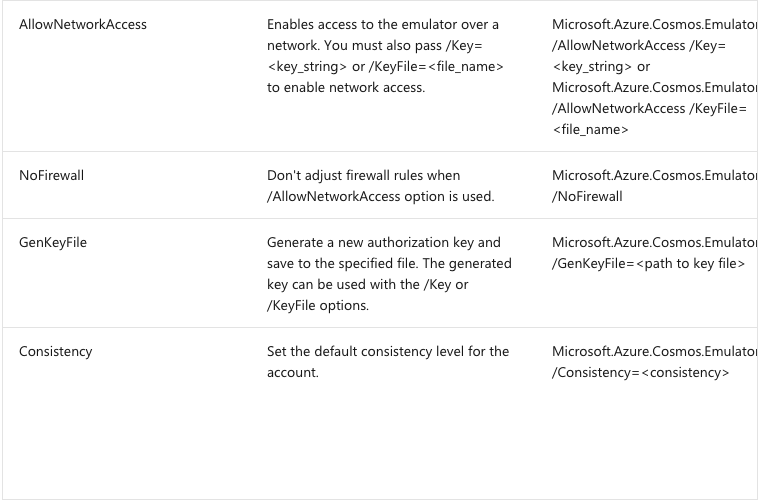
You can run the emulator on a local network. To enable network access, specify the /AllowNetworkAccess option at the command-line, which also requires that you specify /Key=key_string or /KeyFile=file_name. You can use /GenKeyFile=file_name to generate a file with a random key upfront. Then you can pass that to /KeyFile=file_name or /Key=contents_of_file.
To enable network access for the first time the user should shut down the emulator and delete the emulator's data directory (%LOCALAPPDATA%\CosmosDBEmulator).
Developing with the emulator
SQL API
Once you have the Azure Cosmos Emulator running on your desktop, you can use any supported Azure Cosmos DB SDK or the Azure Cosmos DB REST API to interact with the emulator. The Azure Cosmos Emulator also includes a built-in Data Explorer that lets you create containers for SQL API or Cosmos DB for Mongo DB API, and view and edit items without writing any code.
// Connect to the Azure Cosmos Emulator running locally
DocumentClient client = new DocumentClient(
new Uri("https://localhost:8081"), "C2y6yDjf5/R+ob0N8A7Cgv30VRDJIWEHLM+4QDU5DE2nQ9nDuVTqobD4b8mGGyPMbIZnqyMsEcaGQy67XIw/Jw==");
Azure Cosmos DB's API for MongoDB
Once you have the Azure Cosmos Emulator running on your desktop, you can use the Azure Cosmos DB's API for MongoDB to interact with the emulator. Start emulator from command prompt as an administrator with "/EnableMongoDbEndpoint". Then use the following connection string to connect to the MongoDB API account:
mongodb://localhost:C2y6yDjf5/R+ob0N8A7Cgv30VRDJIWEHLM+4QDU5DE2nQ9nDuVTqobD4b8mGGyPMbIZnqyMsEcaGQy67XIw/Jw==@localhost:10255/admin?ssl=true
Table API
Once you have the Azure Cosmos Emulator running on your desktop, you can use the Azure Cosmos DB Table API SDK to interact with the emulator. Start emulator from command prompt as an administrator with "/EnableTableEndpoint". Next run the following code to connect to the table API account:
using Microsoft.WindowsAzure.Storage;
using Microsoft.WindowsAzure.Storage.Table;
using CloudTable = Microsoft.WindowsAzure.Storage.Table.CloudTable;
using CloudTableClient = Microsoft.WindowsAzure.Storage.Table.CloudTableClient;
string connectionString = "DefaultEndpointsProtocol=http;AccountName=localhost;AccountKey=C2y6yDjf5/R+ob0N8A7Cgv30VRDJIWEHLM+4QDU5DE2nQ9nDuVTqobD4b8mGGyPMbIZnqyMsEcaGQy67XIw/Jw==;TableEndpoint=http://localhost:8902/;";
CloudStorageAccount account = CloudStorageAccount.Parse(connectionString);
CloudTableClient tableClient = account.CreateCloudTableClient();
CloudTable table = tableClient.GetTableReference("testtable");
table.CreateIfNotExists();
table.Execute(TableOperation.Insert(new DynamicTableEntity("partitionKey", "rowKey")));
Cassandra API
Start emulator from an administrator command prompt with "/EnableCassandraEndpoint". Alternatively you can also set the environment variable AZURE_COSMOS_EMULATOR_CASSANDRA_ENDPOINT=true.
Run the following commands in a regular command prompt window: BashCopy set Path=c:\Python27;%Path% cd /d C:\sdk\apache-cassandra-3.11.3\bin set SSL_VERSION=TLSv1_2 set SSL_VALIDATE=false cqlsh localhost 10350 -u localhost -p C2y6yDjf5/R+ob0N8A7Cgv30VRDJIWEHLM+4QDU5DE2nQ9nDuVTqobD4b8mGGyPMbIZnqyMsEcaGQy67XIw/Jw== --ssl
In the CQLSH shell, run the following commands to connect to the Cassandra endpoint: BashCopy CREATE KEYSPACE MyKeySpace WITH replication = {'class':'MyClass', 'replication_factor': 1}; DESCRIBE keyspaces; USE mykeyspace; CREATE table table1(my_id int PRIMARY KEY, my_name text, my_desc text); INSERT into table1 (my_id, my_name, my_desc) values( 1, 'name1', 'description 1'); SELECT * from table1; EXIT
Gremlin API
Start emulator from an administrator command prompt with "/EnableGremlinEndpoint". Alternatively you can also set the environment variable AZURE_COSMOS_EMULATOR_GREMLIN_ENDPOINT=true
In the emulator's Data Explorer create a database "db1" and a collection "coll1"; for the partition key, choose "/name"
Run the following commands in a regular command prompt window: BashCopy cd /d C:\sdk\apache-tinkerpop-gremlin-console-3.3.4-bin\apache-tinkerpop-gremlin-console-3.3.4 copy /y conf\remote.yaml conf\remote-localcompute.yaml notepad.exe conf\remote-localcompute.yaml hosts: [localhost] port: 8901 username: /dbs/db1/colls/coll1 password: C2y6yDjf5/R+ob0N8A7Cgv30VRDJIWEHLM+4QDU5DE2nQ9nDuVTqobD4b8mGGyPMbIZnqyMsEcaGQy67XIw/Jw== connectionPool: { enableSsl: false} serializer: { className: org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.driver.ser.GraphSONMessageSerializerV1d0, config: { serializeResultToString: true }} bin\gremlin.bat
In the Gremlin shell run the following commands to connect to the Gremlin endpoint: BashCopy :remote connect tinkerpop.server conf/remote-localcompute.yaml :remote console :> g.V() :> g.addV('person1').property(id, '1').property('name', 'somename1') :> g.addV('person2').property(id, '2').property('name', 'somename2') :> g.V()
Export the TLS/SSL certificate
.NET languages and runtime use the Windows Certificate Store to securely connect to the Azure Cosmos DB local emulator. Other languages have their own method of managing and using certificates. Java uses its own certificate store whereas Python uses socket wrappers.
In order to obtain a certificate to use with languages and runtimes that do not integrate with the Windows Certificate Store, you will need to export it using the Windows Certificate Manager. You can start it by running certlm.msc or follow the step by step instructions in Export the Azure Cosmos Emulator Certificates. Once the certificate manager is running, open the Personal Certificates as shown below and export the certificate with the friendly name "DocumentDBEmulatorCertificate" as a BASE-64 encoded X.509 (.cer) file.
The X.509 certificate can be imported into the Java certificate store by following the instructions in Adding a Certificate to the Java CA Certificates Store. Once the certificate is imported into the certificate store, clients for SQL and Azure Cosmos DB's API for MongoDB will be able to connect to the Azure Cosmos Emulator.
When connecting to the emulator from Python and Node.js SDKs, TLS verification is disabled.
Command-line tool reference
From the installation location, you can use the command-line to start and stop the emulator, configure options, and perform other operations.
Command-line syntax
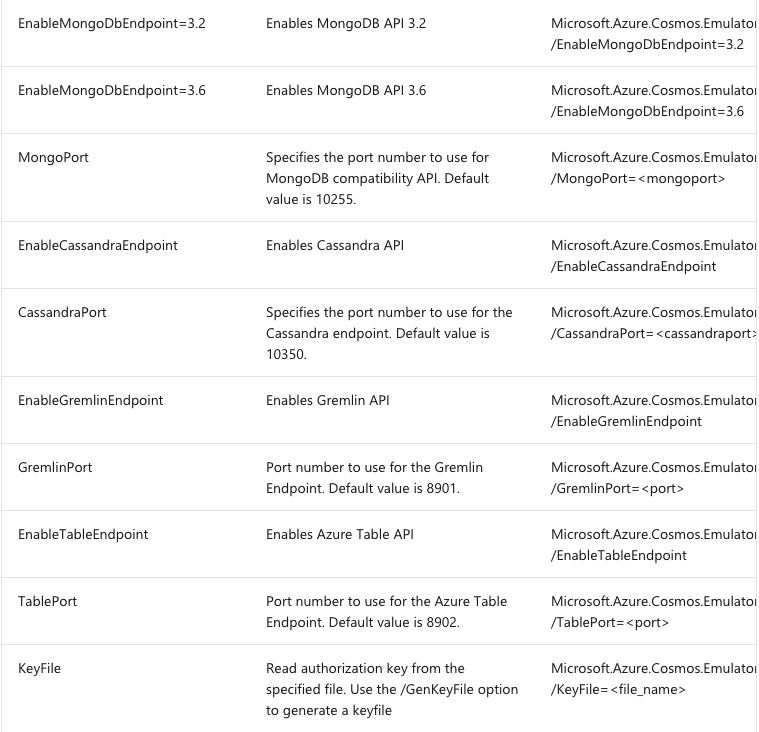
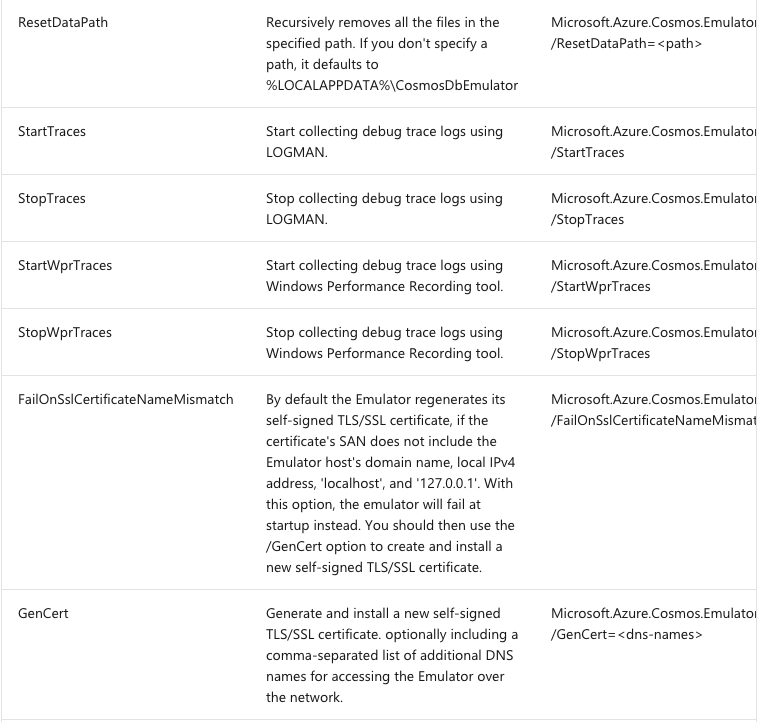
Microsoft.Azure.Cosmos.Emulator.exe [/Shutdown] [/DataPath] [/Port] [/MongoPort] [/DirectPorts] [/Key] [/EnableRateLimiting] [/DisableRateLimiting] [/NoUI] [/NoExplorer] [/EnableMongoDbEndpoint] [/?]
To view the list of options, type Microsoft.Azure.Cosmos.Emulator.exe /? at the command prompt.
Change the number of containers
By default, you can create up to 25 fixed size containers (only supported using Azure Cosmos DB SDKs), or 5 unlimited containers using the Azure Cosmos Emulator. By modifying the PartitionCount value, you can create up to 250 fixed size containers or 50 unlimited containers, or any combination of the two that does not exceed 250 fixed size containers (where one unlimited container = 5 fixed size containers).
However it's not recommended to set up the emulator to run with more than 200 fixed size containers. Because of the overhead that it adds to the disk IO operations, which result in unpredictable timeouts when using the endpoint APIs.
If you attempt to create a container after the current partition count has been exceeded, the emulator throws a ServiceUnavailable exception, with the following message.
"Sorry, we are currently experiencing high demand in this region, and cannot fulfill your request at this time. We work continuously to bring more and more capacity online, and encourage you to try again. ActivityId: 12345678-1234-1234-1234-123456789abc"
To change the number of containers available in the Azure Cosmos Emulator, run the following steps:
Delete all local Azure Cosmos Emulator data by right-clicking the Azure Cosmos DB Emulator icon on the system tray, and then clicking Reset Data….
Delete all emulator data in this folder %LOCALAPPDATA%\CosmosDBEmulator.
Exit all open instances by right-clicking the Azure Cosmos DB Emulator icon on the system tray, and then clicking Exit. It may take a minute for all instances to exit.
Install the latest version of the Azure Cosmos Emulator.
Launch the emulator with the PartitionCount flag by setting a value <= 250. For example: C:\Program Files\Azure Cosmos DB Emulator> Microsoft.Azure.Cosmos.Emulator.exe /PartitionCount=100.
Controlling the emulator
The emulator comes with a PowerShell module to start, stop, uninstall, and retrieve the status of the service. Run the following cmdlet to use the PowerShell module:
Import-Module "$env:ProgramFiles\Azure Cosmos DB Emulator\PSModules\Microsoft.Azure.CosmosDB.Emulator"
or place the PSModules directory on your PSModulesPath and import it as shown in the following command:
$env:PSModulesPath += "$env:ProgramFiles\Azure Cosmos DB Emulator\PSModules"
Import-Module Microsoft.Azure.CosmosDB.Emulator
Here is a summary of the commands for controlling the emulator from PowerShell:
Get-CosmosDbEmulatorStatus
Syntax
Get-CosmosDbEmulatorStatus
Remarks
Returns one of these ServiceControllerStatus values: ServiceControllerStatus.StartPending, ServiceControllerStatus.Running, or ServiceControllerStatus.Stopped.
Start-CosmosDbEmulator
Syntax
Start-CosmosDbEmulator [-DataPath <string>] [-DefaultPartitionCount <uint16>] [-DirectPort <uint16[]>] [-MongoPort <uint16>] [-NoUI] [-NoWait] [-PartitionCount <uint16>] [-Port <uint16>] [<CommonParameters>]
Remarks
Starts the emulator. By default, the command waits until the emulator is ready to accept requests. Use the -NoWait option, if you wish the cmdlet to return as soon as it starts the emulator.
Stop-CosmosDbEmulator
Syntax
Stop-CosmosDbEmulator [-NoWait]
Remarks
Stops the emulator. By default, this command waits until the emulator is fully shut down. Use the -NoWait option, if you wish the cmdlet to return as soon as the emulator begins to shut down.
Uninstall-CosmosDbEmulator
Syntax
Uninstall-CosmosDbEmulator [-RemoveData]
Remarks
Uninstalls the emulator and optionally removes the full contents of $env:LOCALAPPDATA\CosmosDbEmulator. The cmdlet ensures the emulator is stopped before uninstalling it.
Running on Docker
The Azure Cosmos Emulator can be run on Docker for Windows. The emulator does not work on Docker for Oracle Linux.
Once you have Docker for Windows installed, switch to Windows containers by right-clicking the Docker icon on the toolbar and selecting Switch to Windows containers.
Next, pull the emulator image from Docker Hub by running the following command from your favorite shell.
docker pull mcr.microsoft.com/cosmosdb/windows/azure-cosmos-emulator
To start the image, run the following commands.
From the command-line:
md %LOCALAPPDATA%\CosmosDBEmulator\bind-mount
docker run --name azure-cosmosdb-emulator --memory 2GB --mount "type=bind,source=%LOCALAPPDATA%\CosmosDBEmulator\bind-mount,destination=C:\CosmosDB.Emulator\bind-mount" --interactive --tty -p 8081:8081 -p 8900:8900 -p 8901:8901 -p 8902:8902 -p 10250:10250 -p 10251:10251 -p 10252:10252 -p 10253:10253 -p 10254:10254 -p 10255:10255 -p 10256:10256 -p 10350:10350 mcr.microsoft.com/cosmosdb/windows/azure-cosmos-emulator
Note: If you see a port conflict error (specified port is already in use) when you run the docker run command, you can pass a custom port by altering the port numbers. For example, you can change the "-p 8081:8081" to "-p 443:8081"
From PowerShell:
md $env:LOCALAPPDATA\CosmosDBEmulator\bind-mount 2>null
docker run --name azure-cosmosdb-emulator --memory 2GB --mount "type=bind,source=$env:LOCALAPPDATA\CosmosDBEmulator\bind-mount,destination=C:\CosmosDB.Emulator\bind-mount" --interactive --tty -p 8081:8081 -p 8900:8900 -p 8901:8901 -p 8902:8902 -p 10250:10250 -p 10251:10251 -p 10252:10252 -p 10253:10253 -p 10254:10254 -p 10255:10255 -p 10256:10256 -p 10350:10350 mcr.microsoft.com/cosmosdb/windows/azure-cosmos-emulator
The response looks similar to the following:
Starting emulator
Emulator Endpoint: https://172.20.229.193:8081/
Master Key: C2y6yDjf5/R+ob0N8A7Cgv30VRDJIWEHLM+4QDU5DE2nQ9nDuVTqobD4b8mGGyPMbIZnqyMsEcaGQy67XIw/Jw==
Exporting SSL Certificate
You can import the SSL certificate from an administrator command prompt on the host by running:
cd /d %LOCALAPPDATA%\CosmosDBEmulatorCert
powershell .\importcert.ps1
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Starting interactive shell
Now use the endpoint and master key-in from the response in your client and import the TLS/SSL certificate into your host. To import the TLS/SSL certificate, do the following from an admin command prompt:
From the command-line:
cd %LOCALAPPDATA%\CosmosDBEmulator\bind-mount
powershell .\importcert.ps1
From PowerShell:
cd $env:LOCALAPPDATA\CosmosDBEmulator\bind-mount
.\importcert.ps1
Closing the interactive shell once the emulator has been started will shut down the emulator's container.
To open the Data Explorer, navigate to the following URL in your browser. The emulator endpoint is provided in the response message shown above.
https://<emulator endpoint provided in response>/_explorer/index.html
If you have a .NET client application running on a Linux docker container and if you are running Azure Cosmos emulator on a host machine, please follow the below section for Linux to import the certificate into the Linux docker container.
Running on Mac or Linux
Currently the Cosmos emulator can only be run on Windows. Users running Mac or Linux can run the emulator in a Windows virtual machine hosted a hypervisor such as Parallels or VirtualBox. Below are the steps to enable this.
Within the Windows VM run the command below and make note of the IPv4 address.
ipconfig.exe
Within your application you need to change the URI used as Endpoint to use the IPv4 address returned by ipconfig.exe instead of localhost.
The next step, from the within the Windows VM, launch the Cosmos emulator from the command line using the following options.
Microsoft.Azure.Cosmos.Emulator.exe /AllowNetworkAccess /Key=C2y6yDjf5/R+ob0N8A7Cgv30VRDJIWEHLM+4QDU5DE2nQ9nDuVTqobD4b8mGGyPMbIZnqyMsEcaGQy67XIw/Jw==
Finally, we need to import the Emulator CA certificate into the Linux or Mac environment.
Linux
If you are working on Linux, .NET relays on OpenSSL to do the validation:
Export the certificate in PFX format (PFX is available when choosing to export the private key).
Copy that PFX file into your Linux environment.
Convert the PFX file into a CRT file BashCopy openssl pkcs12 -in YourPFX.pfx -clcerts -nokeys -out YourCTR.crt
Copy the CRT file to the folder that contains custom certificates in your Linux distribution. Commonly on Debian distributions, it is located on /usr/local/share/ca-certificates/. BashCopy cp YourCTR.crt /usr/local/share/ca-certificates/
Update the CA certificates, which will update the /etc/ssl/certs/ folder. BashCopy update-ca-certificates
Mac OS
Use the following steps if you are working on Mac:
Export the certificate in PFX format (PFX is available when choosing to export the private key).
Copy that PFX file into your Mac environment.
Open the Keychain Access application and import the PFX file.
Open the list of Certificates and identify the one with the name localhost.
Open the context menu for that particular item, select Get Item and under Trust > When using this certificate option, select Always Trust.
After following these steps, your environment will trust the certificate used by the Emulator when connecting to the IP address exposes by /AllowNetworkAccess.
Troubleshooting
Use the following tips to help troubleshoot issues you encounter with the Azure Cosmos Emulator:
If you installed a new version of the emulator and are experiencing errors, ensure you reset your data. You can reset your data by right-clicking the Azure Cosmos Emulator icon on the system tray, and then clicking Reset Data…. If that does not fix the errors, you can uninstall the emulator and any older versions of the emulator if found, remove "C:\Program files\Azure Cosmos DB Emulator" directory and reinstall the emulator. See Uninstall the local emulator for instructions.
If the Azure Cosmos Emulator crashes, collect dump files from '%LOCALAPPDATA%\CrashDumps' folder, compress them, and open a support ticket from the Azure portal.
If you experience crashes in Microsoft.Azure.Cosmos.ComputeServiceStartupEntryPoint.exe, this might be a symptom where the Performance Counters are in a corrupted state. Usually running the following command from an admin command prompt fixes the issue: cmdCopy lodctr /R
If you encounter a connectivity issue, collect trace files, compress them, and open a support ticket in the Azure portal.
If you receive a Service Unavailable message, the emulator might be failing to initialize the network stack. Check to see if you have the Pulse secure client or Juniper networks client installed, as their network filter drivers may cause the problem. Uninstalling third-party network filter drivers typically fixes the issue. Alternatively, start the emulator with /DisableRIO, which will switch the emulator network communication to regular Winsock.
While the emulator is running, if your computer goes to sleep mode or runs any OS updates, you might see a Service is currently unavailable message. Reset the emulator's data, by right-clicking on the icon that appears on the windows notification tray and select Reset Data.
Collect trace files
To collect debugging traces, run the following commands from an administrative command prompt:
cd /d "%ProgramFiles%\Azure Cosmos DB Emulator"
Microsoft.Azure.Cosmos.Emulator.exe /shutdown. Watch the system tray to make sure the program has shut down, it may take a minute. You can also just click Exit in the Azure Cosmos Emulator user interface.
Microsoft.Azure.Cosmos.Emulator.exe /startwprtraces
Microsoft.Azure.Cosmos.Emulator.exe
Reproduce the problem. If Data Explorer is not working, you only need to wait for the browser to open for a few seconds to catch the error.
Microsoft.Azure.Cosmos.Emulator.exe /stopwprtraces
Navigate to %ProgramFiles%\Azure Cosmos DB Emulator and find the docdbemulator_000001.etl file.
Open a support ticket in the Azure portal and include the .etl file along with repro steps.
Uninstall the local emulator
Exit all open instances of the local emulator by right-clicking the Azure Cosmos Emulator icon on the system tray, and then clicking Exit. It may take a minute for all instances to exit.
In the Windows search box, type Apps & features and click on the Apps & features (System settings) result.
In the list of apps, scroll to Azure Cosmos DB Emulator, select it, click Uninstall, then confirm and click Uninstall again.
When the app is uninstalled, navigate to %LOCALAPPDATA%\CosmosDBEmulator and delete the folder.
Next steps
In this tutorial, you've learned how to use the local emulator for free local development. You can now proceed to the next tutorial and learn how to export emulator TLS/SSL certificates.
Source:Paper.li
















Comments