Understanding Workflow Of OAuth2.0 Authorization Grant Types
- The Tech Platform

- Oct 22, 2020
- 6 min read
Introduction
OAuth is an open standard used for authorization; i.e. to grant access to functionality/data/etc. without having to deal with the original authentication. It allows a user to grant access to a client application to the user's protected resources, without revealing user credentials. These resources could be photos or contacts that are usually stored resource servers. OAuth does it this by granting the requesting client application a token, after user approves access. Each token grants limited access to specified resources for a specific period. This article demonstrates basic workflow of various authorization grant types in OAuth2.0 framework.
Different Types of Authorization Grants
The application that uses an OAuth flow to get an access token and then which flow we use will depends on what kind of app it is -- things like where it is deployed and other properties about the app. There are four Authorization grant types defined and used in different contexts.
Authorization Code: Used for back-end web apps, native apps
Implicit: Used for SPA app executing on the user's browser.
Client Credential: Used for machine-to-machine authentication or service accounts where there isn't a user involved
Resource Owner Password Credential: Used for highly trusted apps, not recommended.
Actors in OAuth2.0 workflow
User/Resource Owner Owner of a user resource; i.e. end-user, who is giving access to some portion of his/her account.
User-Agent Browser or native app.
Client Application The application that is attempting to get access to the user’s account or a resource on Resource Server i.e. APIs. This application could be website, desktop or mobile app.
Authorization Server The server where the client applications are registered. It holds user identities, authenticates a user, and asks him/her to grant client app to access protected resource hosted by a resource server and then issuing an access token to client app.
Resource Server The Web API or web service that hosts the secured and protected user resources and protected by OAuth. It shares user resources with client app in possession of an appropriate access token.
Authorization server endpoints
To generate access token, authorization server uses two endpoints,
Authorization endpoint - used by the client to obtain authorization from the resource owner via user-agent redirection.
Token endpoint - used by the client to exchange an authorization grant for an access token, typically with client authentication.
Workflow of Authorization Code Grant Type
This grant type is commonly used because it is optimized for server side web based application where source code not publicly exposed and client secret confidentiality can be maintained. This is redirection-based flow where authorization code routed through user agent. The authorization code grant type is used to obtain both access tokens and refresh tokens.
Client Application Registration
Before using OAuth, client application must be registered into authorization server with below information,
Application Name
Application Website
Redirect URI or Callback URL
The redirect URI is where service will redirect after authorization or denial by authorization server. Once the client is being registered in authorization server, authorization server will provide Client ID and Client secret to client, and then the client will use this while requesting any resources for a user. The client id is the publicly exposed string that is used by the authorization server to identify the client application. The client secret must be kept private between client and authorization server and used to authenticate client app when client is requesting for user resources. Below workflow diagram of authorization code grant type is self-explanatory and demonstrates how access token is generated from authorization server and the same token is used to access protected resources.
Step I - Calling Authorization endpoint by client application The user is using the browser and visiting the client website and they click the login button to use the app. Client redirects the request to Auth Server by calling authorized endpoint to grant user access and request an authorization code. response_type should be set as code while calling authorize endpoint.
Method: POST
Content-Type: application/x-www.form-urlencoded
URL: https://your-authserver.com/authorize?
response_type=code
&client_id=<<Client_ID>>
&redirect_uri=<https://clientapp.com/callback>>
&scope=<<photo+offline_access>>
&state=<<iX15fHJ415VMLClp>> Here,
response_type=code: Indicates that your app expect to receive an authorization code.
client_id: The Client identifier provided by Auth Server.
redirect_uri: Indicates the URL to return after authorization is complete. This is nothing but a callback url.
Scope: A space separated string indicating which parts of the user account you wish to access.
State: A random string generated by your application, which you will verify later.
Step II - User Authorize the client application Auth Server requests for credentials to user and asks him/her to approve consent. Sample login screen for your reference.
User entered credentials and is granted consent. Sample consent screen for your reference.
Step III - Client application receives authorization code Auth server redirects request to user agent to the application redirect URI, which was specified during client registration with an authorization code that's a one-time use time limited code and that goes back into the browser, the browser then delivers it back to the client application saying here's the temporary code. Now the application can use this code to get an access token.
https://clientapp.com/callback?
state=iX15fHJ415VMLClp
&code=5HcrmpuvvY98gZQw_gq9MivXui97kTaaLPQvGnj3x4o9sOhk Verify state query parameters in the URL. It should match with the value stored in this user's session so that will protect against CSRF attacks. Step IV - Exchange authorization code to retrieve access token The application's web server will go and talk to the OAuth server again with this authorization code to get an access token along with client authentication details including client id and client secrets and do a POST request to the token endpoint. grant_type should be set as authorization_code while calling token endpoint.
Method: POST
Content-Type: application/x-www.form-urlencoded
URL: https://your-authserver.com/token?
grant_type=authorization_code
&client_id=wP_wLcKoURU8U_dELDYuGzvE
&client_secret=nnlTJLSMCp2yiVM74HTgSHL4YTSvZJsSVi6KrFRfsGWOkJa0
&redirect_uri=<<CallabckURL>>
&code=5HcrmpuvvY98gZQw_gq9MivXui97kTaaLPQvGnj3x4o9sOhk Here,
grant_type=authorization_code: Indicates request contains authorization code.
client_id: The Client ID you receive when you first created an application.
client_secret: The Client secret provided by Auth server during registration.
redirect_uri: This should match the redirect URI used in the original request.
code: Include authorization code which is retrieved in the authorized endpoint.
Step V - Application receives access token in response Now client app receives access token and using this token client makes API requests to resource server on behalf of the user. The response includes the access token and refresh token.
{
"token_type": "Bearer",
"expires_in": 86400,
"access_token": "QKY08tqDO8aeNebZbfgUFs1PH-cjerK2WBvE9FZpYGgZHnS_nLfhKYTECMBmPF_chz5GipOA",
"scope": "photo offline_access",
"refresh_token": "8V2dMpzRqB5cQDvoTb6X_Msl"
} Workflow of Implicit Grant Type
This grant type used for mobile app and SPA web applications where the client secret confidentiality is not guaranteed. Using this grant type, instead of issuing the client an authorization code, the client issued an access token directly. This is also a redirection-based flow but the access token is given to the user agent to forward to the client application, so it may be exposed to the user and other applications on the user’s device. In addition, this type do not authenticate the identity of the client application and relies on the redirect URI to serve this purpose. That is why it is having security concern as if access tokens exposed to resource owner and that can be misused. Below workflow diagram of implicit grant type is self-explanatory and demonstrates how access token is generated from authorization server and the same token is used to access protected resources.
Step I - Calling Authorization endpoint by client application The user is using browser and visiting the client website and they click the login button to use the app. Client redirects request to Auth Server by calling authorize endpoint to grant user access and request an authorization code. response_type should be set as token while calling authorize endpoint.
Method: POST
Content-Type: application/x-www.form-urlencoded
URL: https://your-authserver.com/authorize?
response_type=token
&client_id=<Client_ID>
&redirect_uri=<<https://clientapp.com/callback>>
&scope=<<photo+offline_access>>
&state=iX15fHJ415VMLClp Step II - User Authorize the client application Auth Server requests for credentials to user and asks him/her to approve consent. Step III - User-agent receives access token directly with redirect URI User agent directly receives access token in callback url. Here, client does not need to perform extra steps to call token endpoint.
https://clientapp.com/callback?
state=iX15fHJ415VMLClp
&access_token= QKY08tqDO8aeNebZbfgUFs1PH-cjerK2WBvE9FZpYGgZHnS_nLfhKYTECMBmPF_chz5GipOA
&expire_in=3600
&token_type=abc Workflow of Client Credentials Grant Type
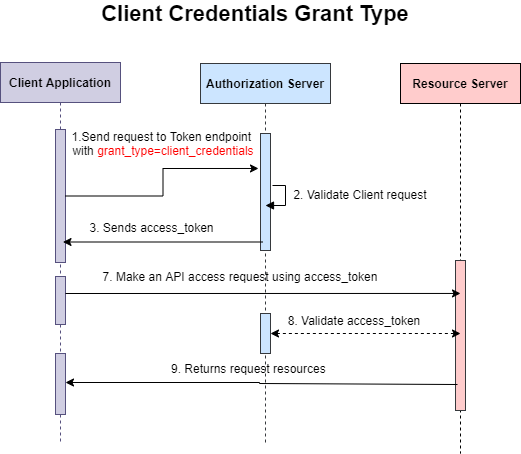
This grant type designed for client application who are resource owner. E.g. Console application or Windows services. Best use case would be machine-to-machine communication and when client and resource owner are the same entity and separate user entity not involved in this workflow. The below workflow diagram of client credentials type is self-explanatory and demonstrates how access token is generated from authorization server and the same token is used to access protected resources.
Step I - Calling Token endpoint by client application Client is directly calling token endpoint to get an access token. grant_type should be set as client_credentials while calling toke endpoint.
Method: POST
Content-Type: application/x-www.form-urlencoded
URL: https://your-authserver.com/token?
grant_type=client_credentials
&client_id=<<CLIENT_ID>>
&client_secret= <<CLIENT_SECRET>>
&scope=<<abc>> Step II - Client application receives access token directly Client receives access token after auth server validating the client request and then client makes API access request using this token.
{
"token_type": "Bearer",
"expires_in": 86400,
"access_token": "QKY08tqDO8aeNebZbfgUFs1PH-cjerK2WBvE9FZpYGgZHnS_nLfhKYTECMBmPF_chz5GipOA",
“state”: “iX15fHJ415VMLClp”
} Workflow of Resource Owner Password Credential Grant Type
Designed for legacy application and should not be used frequently.
The user provides their credentials directly to the client app that uses the credentials to obtain an access token from auth server.
This grant type should be enabled on the authorization server if other flows are not viable. It is only used when application are trusted by user.
Below workflow diagram of password grant type is self-explanatory and demonstrates how access token is generated from authorization server and same token is used to access protected resources.
Step I - Calling Token endpoint by client application Client is directly calling token endpoint to get an access token. grant_type should be set as password while calling toke endpoint.
Method: POST
Content-Type: application/x-www.form-urlencoded
URL: https://your-authserver.com/token?
grant_type=password
&username=<<Username>>
&password= <<Password>>
&scope=<<offline_access>> Step II - Client application receives access token directly Client receives access token after auth server validate the client request and ten client makes API access request using this token.
{
"token_type": "Bearer",
"expires_in": 86400,
"access_token": "QKY08tqDO8aeNebZbfgUFs1PH-cjerK2WBvE9FZpYGgZHnS_nLfhKYTECMBmPF_chz5GipOA",
}
Conclusion
In this article, we saw how different types of authorization grants work internally with client app, auth server and resource server to generate access token and access protected resources in OAuth2.0 framework. Hope you find this information useful! Happy Learning!
Source: C# corner












Comments