If Else Statement in C++
- The Tech Platform

- Mar 11, 2021
- 1 min read
IF
The if statement evaluates the test expression inside the parenthesis ().
If the test expression is evaluated to true, statements inside the body of if are executed.
If the test expression is evaluated to false, statements inside the body of if are not executed.
Syntax:
if(condition){
//code to be executed
}Example:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int number;
printf("Enter an integer: ");
scanf("%d", &number);
// true if number is less than 0if (number < 0) {
printf("You entered %d.\n", number);
}
printf("The if statement is easy.");
return 0;
}Output:
Enter an integer: -2
You entered -2.
The if statement is easy.IF ELSE
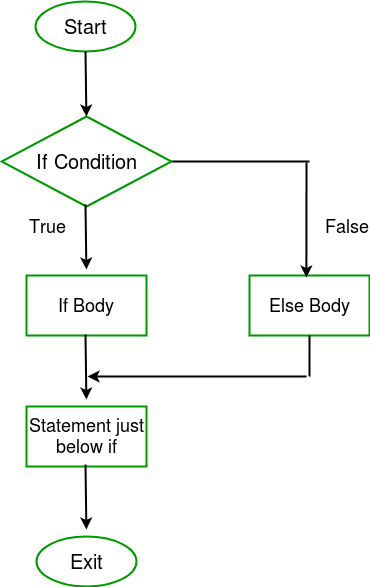
If the test expression is evaluated to true,
statements inside the body of if are executed.
statements inside the body of else are skipped from execution.
If the test expression is evaluated to false,
statements inside the body of else are executed
statements inside the body of if are skipped from execution.
Syntax:
if(condition){
//code if condition is true
}else{
//code if condition is false
} Example:
// Check whether an integer is odd or even
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int number;
printf("Enter an integer: ");
scanf("%d", &number);
// True if the remainder is 0if (number%2 == 0) {
printf("%d is an even integer.",number);
}
else {
printf("%d is an odd integer.",number);
}
return 0;
}Output:
Enter an integer: 7
7 is an odd integer.




Comments